Why stator temperature matters in power plants
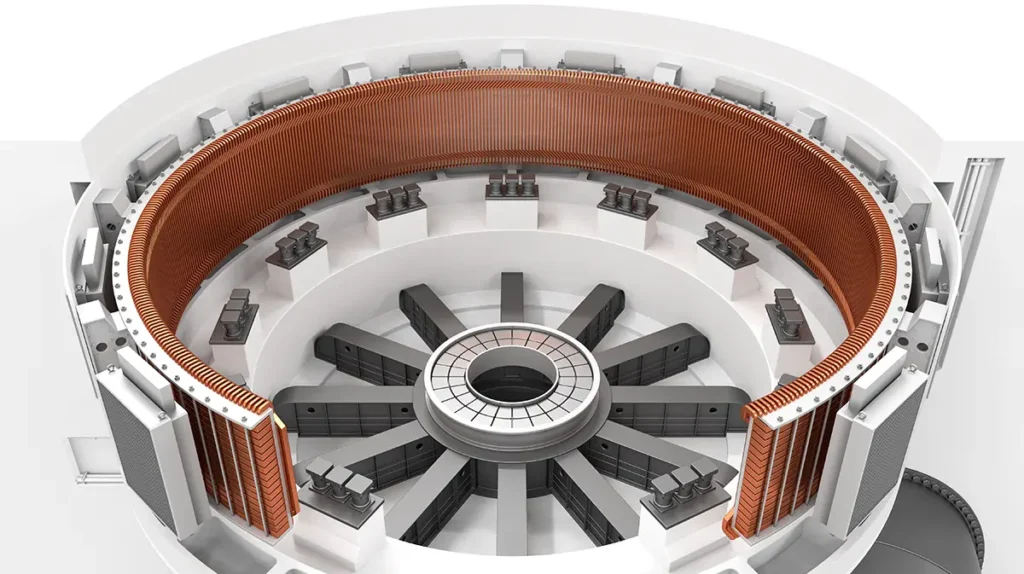
In power generation, generators are key assets that convert mechanical motion into electrical power. As with electric motors, generators use stator windings housed in laminated stator slots, where electrical current flows and heat is inevitably produced. Without precise temperature monitoring, these windings can develop hot spots that degrade insulation, shorten equipment life, or cause catastrophic failure. Stator slot RTD sensors are a proven solution for continuous temperature measurement directly within the stator winding slots.
What are stator slot RTD sensors?
Stator slot RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) sensors are flat, laminated temperature detectors designed to fit between the coils in the stator slots of large generators. Unlike surface-mounted sensors, these RTDs sit in direct contact with winding insulation to capture localized and near real-time temperature data at critical hot-spot locations within the stator
Important distinction between turbines and generators
While turbines themselves generally do not require stator winding RTDs due to their integrated forced cooling fans, generators driven by turbines commonly use stator slot RTDs. Unlike turbines, generators can develop localized hot spots in the stator windings, making embedded temperature monitoring critical for insulation protection and long-term reliability.
How they work in power generation
Stator slot RTDs measure temperature by detecting resistance changes in their sensing element as heat increases in the winding insulation. Typically using platinum elements (Pt100 or Pt1000) with a predictable linear resistance-temperature relationship.
This data is transferred into control or protection systems which can:
- Trigger alarms or automatic shutdown before temperatures reach damaging levels.
- Inform predictive maintenance schedules based on trending thermal behavior.
- Diagnose cooling system issues.
Because stator windings are subject to uneven heating under load, these sensors provide early detection of abnormal conditions. RTD sensors are commonly used for the following benefits they provide in power plant applications.
- Enhanced safety: By continuously monitoring winding temperatures, stator slot RTDs help prevent insulation breakdown and resulting faults that could lead to unplanned outages.
- Increased lifespan: Thermal aging is one of the primary causes of stator winding insulation degradation. Accurate temperature data allows operators to control load and cooling strategies to reduce thermal stress and extend service life.
- Optimized performance: Temperature feedback supports efficient thermal management, ensuring generators operate within safe limits even during peak demand.
- Reduced maintenance costs: Early fault detection means issues can be addressed before they escalate into major repairs. Minimizing insulation or winding damage saves significant maintenance and replacement costs.
Typical power generation applications
Stator slot RTDs are widely used across the power generation sector, including;
- hydroelectric turbines where rapidly changing load conditions can cause significant variations in temperature.
- wind turbine generators, which are exposed to variable wind speeds and dynamic operating loads.
- in thermal and nuclear power plant alternators, stator slot RTDs play a vital role due to the need for continuous, reliable operation and robust temperature monitoring.
In all of these applications, the sensors provide critical early warning of overheating, helping to protect stator insulation systems and ensure uninterrupted power delivery.
Turbines themselves are mechanical machines with continuous forced airflow. This reduces the risk of winding hot spots, making stator slot RTDs unnecessary at that level. Temperature monitoring becomes relevant again once the turbine drives an electrical generator.

Download the stator slot RTD sensor leaflet
Download the stator slot RTD sensor leaflet for a quick overview of its added value, technical specifications, and typical applications.
"*" indicates required fields
